Rigid-Flex PCB vs. Semi-Flex PCB
- Flex Plus Tech team
- Dec 2, 2024
- 4 min read
Updated: Mar 11
Printed circuit boards are super important parts of today’s electronic devices. As tech gets better, we‘ve made all sorts of circuit boards for different uses. Among them, rigid-flexible boards and semi-flexible boards have attracted much attention due to their unique characteristics and functions.
Even though flexible material costs more than rigid ones, rigid-flexible boards are still better because they’re more integrated, perform better, and are more versatile. They also push the limits of design and function.
Moreover, even though flexible materials can change size more than rigid materials, with the continuous advancement of rigid-flexible PCB technology, the problems related to differences in expansion and contraction have been greatly reduced. This reduces the risk of circuit misalignment during the lamination process and improves the overall reliability and long-term durability of the product. In contrast, traditional rigid PCBs may have difficulty meeting the complex needs of compact, high-performance applications. Therefore, rigid-flexible PCBs better meet the growing needs of modern electronic products, making them a wise choice for cutting-edge applications.
Definition and Overview of Semi-flex PCB and Rigid-flex PCB
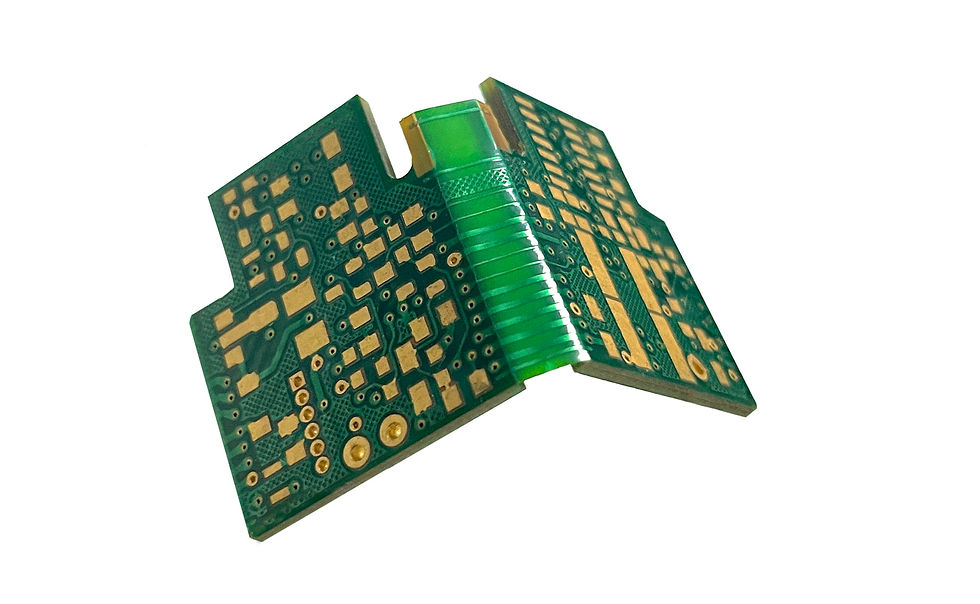
Rigid-Flex PCB
Rigid flex PCB materials usually include soft materials and hard materials, it combines the characteristics of rigid circuit boards and flexible circuit boards. The flexible part is embedded in the rigid part through lamination technology to achieve a structure that can provide mechanical support and adapt to complex 3D layouts. Its basic composition includes multiple rigid layers, flexible layers, and specially treated vias. It is known for its excellent durability and high-density integration capabilities.

Features:
Rigid-flex combination, compact structure.
Supports complex three-dimensional assembly.
Provides excellent electrical performance and signal integrity.
Semi-Flex PCB
A semi-flex PCB is a specially treated rigid circuit board, some areas of which are designed to be bendable to meet certain flexibility requirements. This bending is usually achieved by local thinning or designing special traces on the FR4 substrate. The bending capacity is limited, and most of them are single bends.
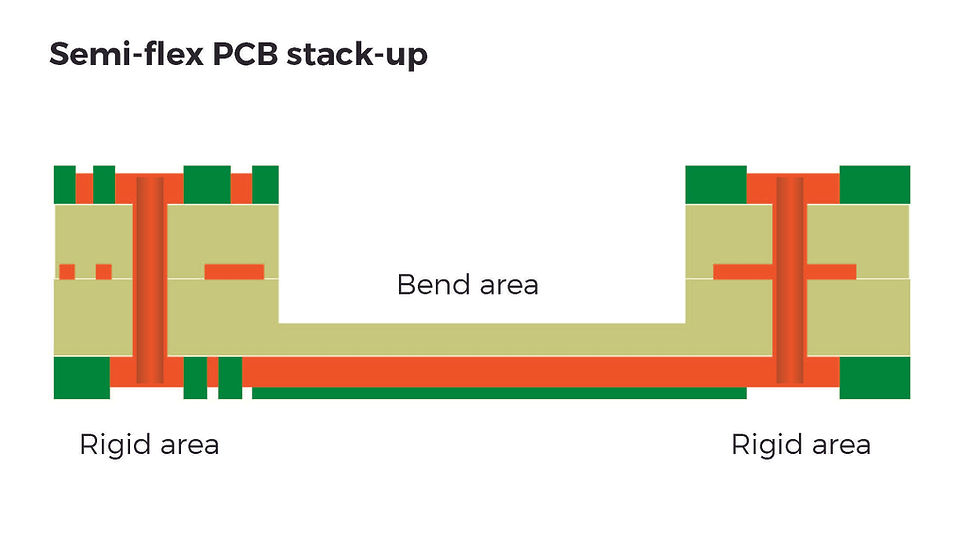
Features:
Partial flexibility, retaining the basic characteristics of rigid PCB.
Relatively simple to manufacture, lower cost than Rigid-flex PCB.
Suitable for limited dynamic or static bending needs.
One of the most crucial differences between Semi-flex and flex PCBs from a design perspective is the fact that a semi-flex PCB can only bend a limited number of times. While regular flexible circuit boards can be bent many times without damage, semi-flexible PCBs will crack or break when bent repeatedly. Therefore, Rigid flex PCBs are best suited for flexible mounting applications. You don't have to worry about the PCB being stressed and damaged due to frequent bending.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Aspect | Rigid-Flex PCB | Semi-Flex PCB |
Advantages | Combines durability and flexibility for complex environments. | Lower manufacturing cost compared to Rigid-Flex. |
| Supports multiple dynamic bends. | Simpler design process, leveraging traditional rigid PCB methods. |
| High integration, eliminating connectors and cables, ensuring signal integrity. | Suitable for single-time bend scenarios, offering good cost-performance balance. |
| Space-efficient, enabling compact and high-density designs. | Ideal for applications with static assembly needs. |
Disadvantages | High manufacturing cost due to complex fabrication processes. | Limited flexibility, unsuitable for dynamic or repeated bending. |
| Requires advanced design expertise and tools. | Reduced durability in the bendable regions over time. |
| Challenging to repair due to its intricate structure. | Restricted to simpler applications and lacks adaptability for 3D layouts. |
Application field
Typical applications of Rigid-Flex PCB

1. Consumer electronics: In smartphones, smart watches, and wearable devices, Rigid-flex PCB is used to achieve compact structure and reliable connection.
2. Medical equipment: In portable medical devices, it not only meets the needs of miniaturization but also provides highly reliable electrical connections.
3. Aerospace and Defense: In applications in harsh environments (such as drones and satellite communication equipment), the reliability of Rigid-flex PCB is critical.
Typical Applications of Semi-Flex PCBs
1. Home appliances: Equipment such as washing machines and refrigerators that require partial flexible connections but no high dynamic bending requirements.
2. Automotive electronics: Flexible connections for fixed positions in the car (such as lighting control modules).
3. Industrial equipment: Suitable for assembly environments with low dynamic requirements, such as sensor modules and panel connections.
How to Decide Between Rigid-Flex and Semi-Flex PCBs?
When you receive a project and don't know which circuit board to use, you can refer to the following:
1. Complex three-dimensional layout: If the design requires high flexibility and complex space management, such as wearable devices or medical devices, a Rigid-Flex PCB is a better choice.
2. Low cost requirements: For cost-sensitive projects such as home appliances or some automotive electronics, Semi-Flex PCB provides high cost performance.
3. Dynamic bending requirements: In scenarios that require multiple dynamic bendings (such as robot arms or sports equipment), Rigid-Flex PCB performs better.
4. Static bending needs: If the bending action only occurs during the assembly process, Semi-Flex PCB is fully capable.
Recommendations:
Long-term investment priority: If the project requires high reliability and durability, choose Rigid-Flex PCB to ensure long-term stability.
Priority when the budget is limited: Semi-flex PCB is suitable for short-term or static demand projects and reduces manufacturing costs.
Summary
Both rigid-flex and semi-flex PCBs have their own advantages, showing different characteristics in terms of flexibility, durability, cost, and application scenarios. Rigid-flex PCBs are suitable for complex and high-performance scenarios due to their high integration and flexibility, while semi-flex PCBs have won the favor of some markets due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of use. When selecting the right type for your project, it is important to clarify project requirements and weigh the pros and cons. Working with a reliable flex PCB supplier can help guide this decision, ensuring you get the best quality and cost-effective solution for your specific needs. The continuous development of these two types of printed circuit boards will continue to promote technological progress in the electronics industry and provide support for diverse applications.

コメント