Application of Flex PCB in Circuit Breakers
- Flex Plus Tech team
- Mar 20
- 4 min read
Updated: Mar 31
With the growing demand for smarter and more compact power systems, flex PCB in circuit breaker design is becoming increasingly important as these core protection devices face higher requirements for integration and reliability. Flex PCB, with its lightweight, flexible, and high-precision wiring characteristics, is emerging as a key technology in circuit breaker design. This article explores the innovative applications of flex PCB in circuit breakers, focusing on its conductive layer design, structural adaptability, and mechanical interconnection solutions.
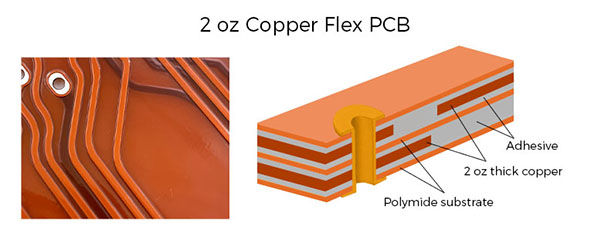
1. Conductive Layer for Flex PCB in Circuit Breaker: 2 oz Copper
In circuit breaker applications, the conductive layer of flex PCB adopts a 2oz (approximately 70μm) rolled copper foil, significantly enhancing current-carrying capacity and heat dissipation. Compared to traditional 1oz copper foil, the 2oz copper layer increases current-carrying capacity by approximately 40%, reducing temperature rise and ensuring stable operation under high short-circuit currents. Additionally, the mechanical strength of the thick copper layer helps resist mechanical vibrations during breaker operation, preventing circuit fractures.
To achieve precise current distribution, the copper layer on the flex PCB undergoes laser etching to form a complex circuit network, integrating current detection and signal transmission functions. This network can also work in coordination with the arc-extinguishing system, optimizing fault response speed.
2. Flex PCB Design: Precise Integration with Circuit Breaker Housing
Modern circuit breaker housings adopt compact modular designs, requiring high space utilization. flex PCB, with its flexible substrate (such as polyimide), can conform to the complex 3D structure of the housing, allowing for customized layouts. Through 3D modeling and simulation, the routing and component arrangement of the flex PCB can seamlessly align with the housing’s inner walls, arc-extinguishing chamber, and operating mechanisms, maximizing space efficiency.
Furthermore, the overall thickness of the flex PCB in circuit breaker can be controlled within 0.4mm to avoid interference with mechanical operations inside the breaker. Its surface is coated with a high-temperature-resistant protective layer (such as a PI cover film), which can withstand the transient high temperatures (typically ≤150°C) generated during breaker operation, ensuring long-term reliability.
3. Through-Hole and Positioning Hole Design
During circuit breaker assembly, flex PCB integrates efficiently with the device through two keyhole structures:
Through-Hole Plug-in Terminals:
The flex PCB in circuit breaker is designed with dense metalized through-holes (typically 0.6-1.0mm in diameter), and a gold-plating of the surface finished process is applied to enhance conductivity and oxidation resistance. These through-holes connect to the breaker’s copper terminals via plug-in connections, using spring pins or crimp terminals for low-impedance electrical contact. The plug-in structure enables fast installation and replacement while preventing soldering defects such as cold solder joints.
Positioning Holes and Snap-Fit Structures:
Non-metalized positioning holes (with a tolerance of ±0.05mm) are distributed along the flex PCB edges and precisely formed through stamping. During assembly, these holes align with nylon positioning posts in the housing, ensuring stable placement even in vibrating environments.
4. Application Advantages and Future Trends
The adoption of flex PCB in circuit breakers offers several significant advantages:
Space Savings: Compared to rigid PCBs, flex PCB reduces volume by over 30%, aiding in miniaturization.
Improved Reliability: An integrated design minimizes cable connection points, reducing contact failure risks.
Cost Optimization: Eliminates traditional wire harness processing steps, enabling automated mass production.
Looking ahead, as flex PCB integrates embedded sensors (such as temperature and strain monitoring), circuit breakers are expected to achieve real-time status monitoring and predictive maintenance, advancing power protection systems toward higher intelligence.

5. Customized Solutions: Flex Plus’s Flex PCB Optimization Practices
In circuit breaker flex PCB design, Flex Plus leverages innovative technology to provide highly customized solutions for clients, further highlighting the cost-effectiveness of flexible circuits. For example, in response to a specific circuit breaker model’s requirements, Flex Plus utilized high-density routing technology and dual-sided functional integration, consolidating current detection and signal control—originally requiring two separate flex PCBs—into a double-sided flex PCB. By optimizing circuit topology, reducing redundant wiring, and employing via-in-pad technology, the circuit area was reduced by 22%, significantly cutting material and assembly costs.
Additionally, custom-shaped cutting allowed a single flex PCB to adapt to multiple functional areas within the circuit breaker while retaining existing positioning holes and terminal insertion slots. This enabled direct assembly upgrades without modifying the housing mold. Testing confirmed that this integrated design helped the client reduce overall costs by approximately 15% while shortening production cycles by 20%, demonstrating the engineering value of flexible circuits in complex electrical systems.
6. Flex PCB Applications in Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers—especially smart circuit breakers or electronic circuit breakers—integrate electronic control modules, sensors, and communication units, requiring high-density wiring and flexible connections. These scenarios are where flex PCBs are commonly used, such as:
Smart Trip Unit Control Board
Modern circuit breakers feature electronic trip units that monitor current, voltage, and temperature and provide precise protection via microprocessors. flex PCBs can connect sensors to the main control chip while adapting to compact spaces.
Communication Modules (e.g., IoT Circuit Breakers)
Circuit breakers with Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or other wireless communication functionalities may incorporate flex PCBs for antenna integration and signal transmission, facilitating compact integration.
Touchscreen/Display Interfaces
High-end circuit breakers with touchscreens or status indicator LEDs use flex PCBs for flexible connections between the display and the main control board.
The application of flexible PCB in circuit breakers, through 2oz thick copper conductive layers, three-dimensional conformal structures, and precision hole positioning, successfully addresses challenges in high current-carrying capability, compact space utilization, and reliable interconnection. This technological approach not only provides innovative design solutions for circuit breakers but also lays the hardware foundation for the intelligent upgrading of power equipment. With continuous advancements in materials and manufacturing processes, flex PCB is poised to play a broader role in the field of power electronics.

Comments